
Back دورة الكربون المحيطية Arabic Cycle du carbone océanique French Океански јаглероден циклус Macedonian 海洋碳循環 Chinese

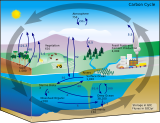
The oceanic carbon cycle (or marine carbon cycle) is composed of processes that exchange carbon between various pools within the ocean as well as between the atmosphere, Earth interior, and the seafloor. The carbon cycle is a result of many interacting forces across multiple time and space scales that circulates carbon around the planet, ensuring that carbon is available globally. The Oceanic carbon cycle is a central process to the global carbon cycle and contains both inorganic carbon (carbon not associated with a living thing, such as carbon dioxide) and organic carbon (carbon that is, or has been, incorporated into a living thing). Part of the marine carbon cycle transforms carbon between non-living and living matter.
Three main processes (or pumps) that make up the marine carbon cycle bring atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) into the ocean interior and distribute it through the oceans. These three pumps are: (1) the solubility pump, (2) the carbonate pump, and (3) the biological pump. The total active pool of carbon at the Earth's surface for durations of less than 10,000 years is roughly 40,000 gigatons C (Gt C, a gigaton is one billion tons, or the weight of approximately 6 million blue whales), and about 95% (~38,000 Gt C) is stored in the ocean, mostly as dissolved inorganic carbon.[1][2] The speciation[clarification needed] of dissolved inorganic carbon in the marine carbon cycle is a primary controller of acid-base chemistry in the oceans.
Earth's plants and algae (primary producers) are responsible for the largest annual carbon fluxes. Although the amount of carbon stored in marine biota (~3 Gt C) is very small compared with terrestrial vegetation (~610 GtC), the amount of carbon exchanged (the flux) by these groups is nearly equal – about 50 GtC each.[1] Marine organisms link the carbon and oxygen cycles through processes such as photosynthesis.[1] The marine carbon cycle is also biologically tied to the nitrogen and phosphorus cycles by a near-constant stoichiometric ratio C:N:P of 106:16:1, also known as the Redfield Ketchum Richards (RKR) ratio,[3] which states that organisms tend to take up nitrogen and phosphorus incorporating new organic carbon. Likewise, organic matter decomposed by bacteria releases phosphorus and nitrogen.
Based on the publications of NASA, World Meteorological Association, IPCC, and International Council for the Exploration of the Sea, as well as scientists from NOAA, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Scripps Institution of Oceanography, CSIRO, and Oak Ridge National Laboratory, the human impacts on the marine carbon cycle are significant.[4][5][6][7] Before the Industrial Revolution, the ocean was a net source of CO2 to the atmosphere whereas now the majority of the carbon that enters the ocean comes from atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2).[8] The burning of fossil fuels and production of cement have changed the balance of carbon dioxide between the atmosphere and oceans,[6] causing acidification of the oceans.[8][9] Climate change, a result of excess CO2 in the atmosphere, has increased the temperature of the ocean and atmosphere (global warming).[10] The slowed rate of global warming occurring from 2000–2010[11] may be attributed to an observed increase in upper ocean heat content.[12][13]
| Part of a series on the |
| Carbon cycle |
|---|
 |
- ^ a b c Schlesinger, William H.; Bernhardt, Emily S. (2013). Biogeochemistry : an analysis of global change (3rd ed.). Waltham, Mass.: Academic Press. ISBN 9780123858740. OCLC 827935936.
- ^ Falkowski, P.; Scholes, R. J.; Boyle, E.; Canadell, J.; Canfield, D.; Elser, J.; Gruber, N.; Hibbard, K.; Högberg, P. (2000-10-13). "The Global Carbon Cycle: A Test of Our Knowledge of Earth as a System". Science. 290 (5490): 291–296. Bibcode:2000Sci...290..291F. doi:10.1126/science.290.5490.291. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 11030643.
- ^ Redfield, Alfred C. (1958). "The Biological Control of Chemical Factors in the Environment". American Scientist. 46 (3): 230A–221. JSTOR 27827150. PMID 24545739.
- ^ Holli, Riebeek (2011-06-16). "The Carbon Cycle: Feature Articles". earthobservatory.nasa.gov. Retrieved 2017-11-30.
- ^ "New report published on "Climate, Carbon and Coral Reefs". World Meteorological Organization. 2015-11-05. Archived from the original on December 18, 2023. Retrieved 2017-11-30.
- ^ a b "Fifth Assessment Report – Climate Change 2013". www.ipcc.ch. Retrieved 2017-11-30.
- ^ "Sabine et al. – The Oceanic Sink for Anthropogenic CO2". www.pmel.noaa.gov. Retrieved 2017-11-30.
- ^ a b Ocean acidification due to increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide (PDF). London: The Royal Society. 2005. ISBN 0-85403-617-2. Retrieved November 17, 2017.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Zeebewas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Fifth Assessment Report – Climate Change 2013". www.ipcc.ch. Retrieved 2017-11-26.
- ^ Knight, J (2009). "Global oceans: Do global temperature trends over the last decade falsify climate predictions?". Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society. 90: S56–S57.
- ^ "Global ocean heat and salt content". www.nodc.noaa.gov. US Department of Commerce, NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information. Retrieved 2017-11-26.
- ^ Guemas, V; Doblas-Reyes, F; Andreu-Burillo, I; Asif, M (2013). "Retrospective prediction of the global warming slowdown in the past decade". Nature Climate Change. 3 (7): 649–653. Bibcode:2013NatCC...3..649G. doi:10.1038/nclimate1863. Archived from the original on 2022-11-25. Retrieved 2019-12-10.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search